See presentation:
https://www.figma.com/file/VqXnUOFKWzz2uH9ZUaq0vZ/MCOM-Presentation?type=design&node-id=1474%3A5879&mode=design&t=lZnlIFJqTKRYtU8P-1
Introduction
With the increasing use of smartphones, the vertical use of videos is becoming more and more important, and as a result, videos in portrait format are also being promoted in social media applications. Younger audiences rarely switch to landscape when using their smartphones, mainly due to discomfort and the subjective feeling that the 16:9 format “looks nicer.” (Pogue, 2018)
Mobile users typically hold their phones vertically about 94% of the time. This preference for the vertical screen orientation of smartphones is driving the production of mobile vertical video content. This format appeals to mobile users because they can easily capture and watch video content without needing to tilt their phone 90 degrees (Mulier et al.,2021).
The Dominance of Mobile Vertical Video Marketing
With the usage of mobile devices, the trend of mobile video becoming the primary way consumers consume content. Indeed, mobile devices are the fastest growing medium for digital marketing, with smartphones driving the overall increase in consumers’ digital content viewing time. Moreover, more than 75% of all video viewing is on mobile devices. Consumers are 1.5 times more likely to watch a video on a smartphone than on a computer. Therefore, video marketers need to rethink their online strategies and implement video marketing more intensively in the mobile space and follow trends such as the vertical video trend (Mulier et al.,2021).
Research Question
“How does the effectiveness of mobile vertical video marketing influence consumer brand attitude in the era of short-form content on social media platforms?”
Paper 1 – “The Effectiveness of Mobile Vertical Video Marketing”
This Way Up: The Effectiveness of Mobile Vertical Video Marketing, Lana Mulier * & Hendrik Slabbinck * & Iris Vermeir, 23 February 2021
In the paper they published three different studies.
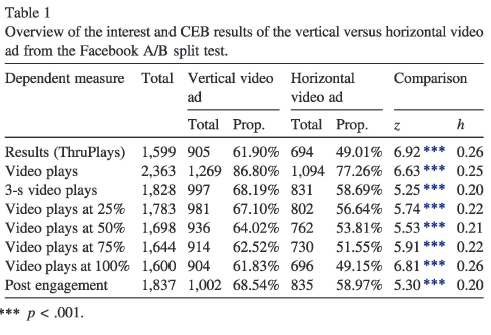
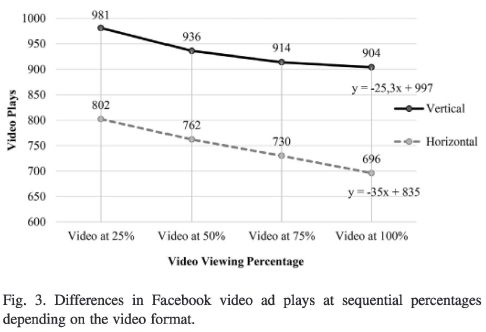
The first one explores the difference in customer engagement behavior between vertical and horizontal advertisements displayed on Facebook. The video duration of the advertisements were 15 seconds and identical in content, with the only distinction being the format. It was revealed that the vertical video was played more frequently (ranging from 25% to 100%) than the horizontal video. The call-to-action button was used at a similar frequency in both cases, suggesting that the format does not appear to be relevant in this context (Mulier et. al.,2021).
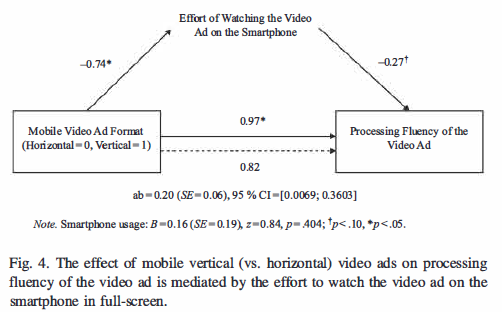
The second study explores the Effect of Mobile Vertical Video Advertising on Processing Fluency Through Effort. They recruited 110 students from a European university (17-29 years). They used two existing 62-s video ads of Nike (2015), which were equal except for the screen format.
After watching the video ad, participants answered two questions on the smartphone. One about the information and the other one about the effort. Participants in the vertical condition said that watching the video on the smartphone takes significantly less effort than in the horizontal condition. The findings from Study 2 confirm that mobile users experience less effort when watching a vertical video ad as opposed to a horizontal video ad, as watching a vertical. Mobile users process the vertical video ad more fluently than the horizontal video ad (Mulier et. al.,2021).
Mobile vertical video ads were found to increase interest, customer engagement behaviors (CEB), and information processing speed compared to traditional horizontal video ads. In addition, mobile vertical video ads were found to have higher completion rates compared to horizontal video ads.
In addition, not all people watch videos on mobile devices, especially members of the older generation. Therefore, to reach a broad audience (without specifically targeting a generation or a certain demographic segment), it is recommended to create two versions of video ads and marketing messages: one for vertical viewing on mobile devices to reach younger viewers, and one horizontal to reach older viewers (Mulier et. al.,2021).
Case Studies on Successful Vertical Video Campaigns
Today, brands use vertical video for everything, from entertainment to educational content on platforms like LinkedIn. With the rise of smartphones, vertical content is transforming how we report and consume world events. Major platforms are promoting vertical video creation and brands are investing in creating compelling content. New interactive features are revolutionizing storytelling and opening up global engagement opportunities (Sharma, 2023).
But besides Mercedes Benz, Netflix and many other brands, Instagram has probably also shaped the trend with its daily vertical stories. In the meantime, Youtube and TikTok have also made the format their own, as they had to keep up with the trend in order not to fall behind (Gilliland, 2019).
Case Study of National Geographics
A very well-known brand where the videos work well, even though one would think they should be played out in wide format for the content, is National Geographic. Despite the nature footage and sometimes long documentaries, the brand has many views on Instagram and was even chosen as a launch partner for IGTV at the time. They created the 47-minutes documentary “One Strange Rock” which generated over three million views (Gilliland., 2019).
National Geographic relies heavily on social media, which accounts for over half of the media company’s advertising revenue. Vertical video, with its appeal to authenticity, is proving to be a key strategy in keeping the audience engaged (ibid.,2023).
For National Geographic, this shift has translated into more content and audience growth, seen on Instagram and TikTok. The brand continues to educate, inform, and inspire while ensuring a profitable business perspective. From the contributor’s perspective, social media has become a valuable tool for sharing behind-the-scenes moments, allowing the audience to connect with the creators and engage in meaningful conversations about the content. In essence, the shift to more authentic, low-fi social media content complements National Geographic’s storytelling by providing a look into the creative process and the people behind the captivating imagery (Barber,2023).
The Influence of Social Media Short Video Marketing
Short video is a new type of video that can be shared, forwarded, and viewed on social media short video platforms within 3 minutes, mainly using mobile intelligent terminals for shooting and editing. The playing time ranges from a few seconds to a few minutes (Liu et al., 2019).
Social media platforms like TikTok, Instagram, and Snapchat provide good access for individuals to watch video clips of short duration, from 15 s to 1 min (Gan et al., 2023).
Paper 2 – “Influence of Social Media Short Video Marketing on Consumer Brand Attitude”
Research on the Influence of Social Media Short Video Marketing on Consumer Brand Attitude, Gao-fu LIU, Yu-chun LI, Peng-chao GAO, Zhuo-ping ZHANG, 2019 August
We can divide short video marketing of social media into three dimensions: interesting content, scene-based experience and user participation and interaction (Liu et al., 2019).
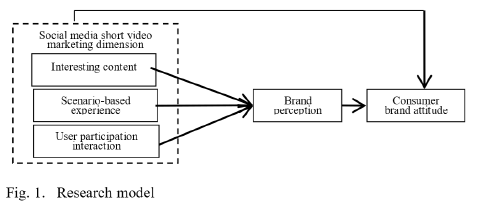
1) Interesting content has a positive impact on brand attitudes. The content with strong interest and high degree of entertainment, integrate the brand culture into the content of extensive entertainment, and enhance consumers’ cognition and emotion of the brand in a relaxed and pleasant way (Liu et al., 2019).
2) Scene-based experience has a positive impact on brand attitude. It can help to provide consumers with a real scene that can be sensed by themselves through complex designed life scenes and consumption scenes, to display brand image fully and variously and spread brand culture, to gain more consumers’ recognition (Liu et al., 2019).
3) User participation interaction has a positive impact on brand attitude. To deepen consumers understanding of the brand and stimulate the positive attitude towards the brand, the content should stimulate more users to participate in the creation and imitation of short video (Liu et al., 2019).
4) Brand perception plays an indirect role in the impact of short video marketing on brand attitude. Short videos should fully consider consumers’ visual and auditory perception, the time and way of brand exposure, and show interesting content and specific experiences to improve consumers’ brand perception and promote positive brand attitude (Liu et al., 2019)
Case Studies
The Critical Perspective
The question is if vertical video is the best option to use videos on mobile devices. Some people might prefer a horizontal viewing mode on large screens (e.g., cinema and television), but like to have a vertical viewing mode on small screens, such as smartphones or smartwatches. Next to the formats we just talked about there are also different one like square video, 360° views, etc. Considering the increasing use of different screen formats only suited for a mobile context (Mulier et. al.,2021).
Critics of the vertical video format argue that vertical video mode violates not only technical video standards, but also the laws of nature concerning human vision. Because our eyes are horizontal, we see the world as a horizontal panorama. Widescreen formats, like in television and movies, allow viewers to use their peripheral vision when watching video, to look at one part of the screen but indirectly see other parts of the screen as well.
It is therefore logical to favor horizontal displays over vertical displays. Indeed, studies of human eye movements show that smooth horizontal pursuit (eye movements that bring the image of a moving object closer to the eyeball) is superior to vertical pursuit. Furthermore, it is intuitively obvious that reading vertical text (vertically aligned letters) is slower than reading horizontal text. However, vertical format is used almost exclusively in print (Mulier et. al.,2021).
Keeping up with ever-changing trends can seem hard these days. Not so long ago, 16:9 widescreen video was the norm, but that changed before most media agencies could catch up.
The next generation device we’ll always be using could be digital glasses or something else that uses landscape orientation.
Also Cinemas will never shoot only in portrait mode because they will always be in landscape mode. Portrait orientation cameras will always be the exception, not the rule.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the appearance of vertical video as a dominant format is reshaping how brands connect with their audiences. With the preference for holding smartphones vertically, mobile users have driven the rise of vertical video content. This shift not only provides a more comfortable viewing experience but also offers to the increasingly popular demand for raw, personality-driven content on social media. Vertical video is a must for companies seeking success in this dynamic environment.
Being vertical doesn’t automatically guarantee success, as the study shows. As long as content is viewed on TVs or laptops, there will always be places for cinematic style of landscape. This means that it should be seen as an additional or alternative format.
The shift to vertical video is a response to habits of today’s audiences. Brands that embrace this change stand to benefit from higher engagement, completion rates, and audience growth.
As we move forward, vertical video is expected to play a crucial role in shaping the future of content creation, sharing, and storytelling on social media platforms.
References:
Napoli M. D. (2016). The “Mobile Effect” on Screen Format: the Case of Vertical Videos. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/311945562_The_Mobile_Effect_on_Screen_Format_the_Case_of_Vertical_Videos
Pogue D. (2018). Video Looks Most Natural Horizontally, but We Hold Our Phones Vertically – We see horizontally but tend to hold our phones vertically. https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/video-looks-most-natural-horizontally-but-we-hold-our-phones-vertically/
Gilliland, Nikki. (2019, November 23). Five examples of brands using vertical video. https://econsultancy.com/brands-vertical-video-social-examples/
Drummond-Butt S.(2019, August 25). Don’t flip that phone: Vertical video is a must for marketers [Infographic]. https://www.impactplus.com/blog/vertical-video-in-marketing-infographic
Liu G., GaoP., Li Y., Zhang Z. (2019, August). Research on the Influence of Social Media Short Video Marketing on Consumer Brand Attitude. Proceedings of the 2019 5th International Conference on Social Science and Higher Education (ICSSHE 2019) 10.2991/icsshe-19.2019.192
Pibert J. (2021). Vertikale Musikvideos. Filmpsychologische Analyse der Wirkung des Hochformats in Lena Meyer-Landruts DON’T LIE TO ME. https://mediarep.org/bitstream/handle/doc/16697/ffk_2021_6_216-228_Pibert_Vertikale_Musikvideos_.pdf?sequence=4&isAllowed=y
Mulier L., Slabbinck H., Vermeir I. (2021, February 23). This Way Up: The Effectiveness of Mobile Vertical Video Marketing. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intmar.2020.12.002
Sharma A. (2023 , January 28). Why are marketers favouring vertical videos more and more? https://www.financialexpress.com/business/brandwagon-why-are-marketers-favouring-vertical-videos-more-and-more-2962645/
Gan J., Shi S.,Filieri R., Leung W. (2023, May 25). Short video marketing and travel intentions: The interplay between visual perspective, visual content, and narration appeal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tourman.2023.104795
Barber K. (2023, October 31). How National Geographic is using its contributor network to refresh its social media channels https://digiday.com/media/how-national-geographic-is-tapping-its-contributor-network-to-refresh-it-social-media-changes/