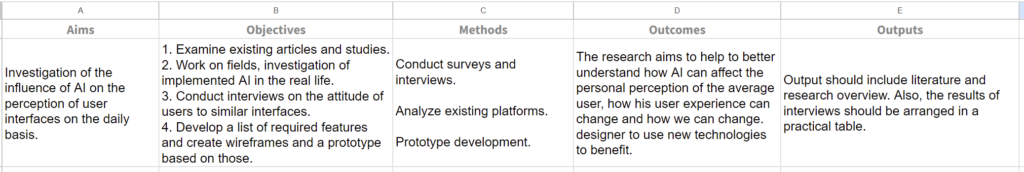
In this article, I would like to briefly explain the differences between the approach to AI development in the US, China and Europe, as it is interesting to see how these global players differ from and influence each other in this field. It could show attitude to new technologies in those countries in generall.
USA: The approach of AI regulations in the USA is largely influenced by the National Artificial Intelligence Initiative (NAII) in 2021. The main goals of these regulations are centered around development, education, and building trust in AI systems. One important aspect is the right of explanation, which ensures transparency in AI decision-making processes.
Risk management is another key aspect of the regulations, which is based on three criteria: assessment, independence, and review. This means that AI systems need to undergo thorough evaluations to identify and mitigate potential risks. Additionally, there is a focus on ensuring independence in the evaluation process and establishing mechanisms for regular reviews.
In terms of development, the regulations prioritize granting full autonomy to AI players. This suggests that there is an emphasis on promoting innovation and allowing AI developers to have the freedom to explore and create within the established regulatory framework.
China: The approach of AI regulations in China is driven by the goal of becoming a leader in the field of artificial intelligence. The government supports a collaborative approach, encouraging the participation of “AI National Champions” in advancing AI technology. The regulations primarily focus on three main goals or topics: development, national security, and gaining an international advantage.
In terms of development, there are relatively few restrictions imposed on AI developers, allowing them a considerable amount of freedom to innovate and create. The emphasis is on fostering a supportive environment for AI research and development, enabling rapid technological advancements.
National security is also a key concern, with regulations aiming to ensure that AI technologies do not pose risks or threats to the country’s security.
Lastly, gaining an international advantage is a priority, suggesting a focus on fostering competitiveness in the global AI market. The regulations likely aim to promote the growth of Chinese AI companies and encourage their expansion and influence beyond national borders.
Europe: The approach of AI regulations in Europe is strongly influenced by the GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), which plays a significant role in establishing rules. A risk-based approach is followed, categorizing regulations into four levels based on the potential risks associated with AI applications. The priority is to ensure user safety, and AI systems are not allowed to make significant decisions autonomously. The right of explanation is considered highly important, emphasizing the need for transparency in AI decision-making processes.
Regulations address the issue of deepfakes and similar techniques by requiring a disclosure comment to be attached to such content. Social scoring using AI is prohibited, aiming to prevent discriminatory or unfair practices. Certain areas are subject to a ban on AI applications, likely for reasons of ethical concerns or potential risks.
However, this approach has faced criticism for being perceived as “not flexible.” This criticism likely suggests that the regulations may be considered rigid or lacking adaptability to address emerging challenges or technological advancements in the AI field.
These diverse approaches are not isolated but mutually influence each other. The competitive nature of the global AI market and the desire to lead in technological advancements create a dynamic where regions learn from one another’s experiences and adapt their regulations accordingly. Cultural, political, and economic factors play a significant role in shaping these approaches, reflecting the unique values and priorities of each region.
Experts advise that Europe should adopt a more flexible approach to AI regulations while the USA should enhance privacy protections by adopting stricter measures. In order to achieve these goals, several recommendations have been put forth:
These include encouraging the sharing of documentation to enhance transparency, promoting collaborative research efforts, establishing standards for AI development, creating AI sandboxes for safe experimentation, supporting large-scale public AI research projects and open-source tools, facilitating regulator-to-regulator exchanges, and developing an AI assurance ecosystem for accountability and trust. By implementing these recommendations, both regions can foster innovation, ensure responsible AI development, and promote international cooperation and harmonization in AI regulations.
As you can see, there is still a long way to go before the global players arrive at a universal approach, but the first steps have already been taken.
References:
The EU and U.S. diverge on AI regulation: A transatlantic comparison and steps to alignment | Brookings. (2023, 24. Juni). Brookings. https://www.brookings.edu/research/the-eu-and-us-diverge-on-ai-regulation-a-transatlantic-comparison-and-steps-to-alignment/
Grunitz, M. (2021, 17. Dezember). AI regulation: EU, USA & China – WeAreBrain Blog. WeAreBrain Blog. https://wearebrain.com/blog/ai-data-science/ai-regulation-eu-usa-china/
AI Regulation News | European Union | USA | China. (o. D.). https://www.airegulation.news/