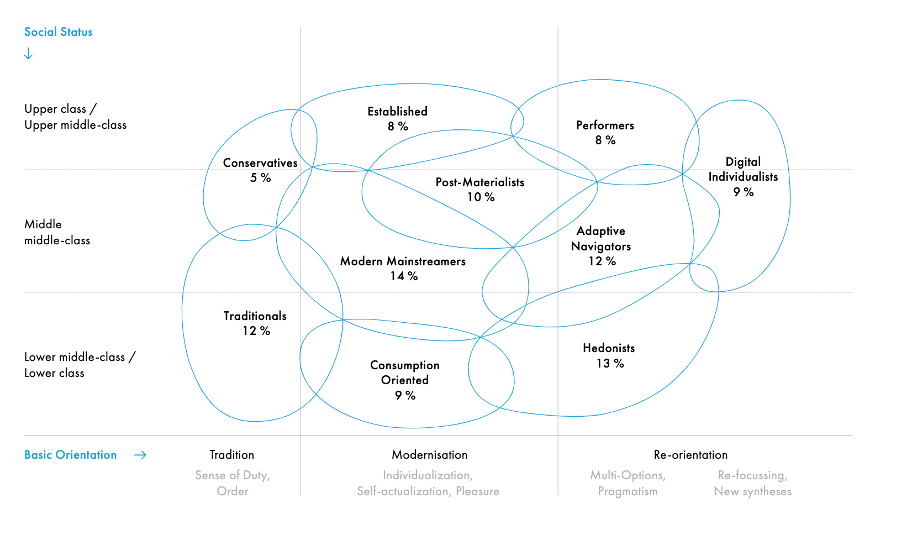
The classic way of media planning is planning according to buyer and user target groups in the corresponding product or service area.
Target groups can be defined using demographic characteristics. Different age groups, genders or occupational groups differ significantly in their behavior.
In recent years, qualitative target group models have increasingly found their way into marketing planning. There enables communication planning differentiated according to values, lifestyles and preferences, which in turn takes into account the psychologically different brand positions in the target group definitions.
One of the Psychographic target group models is Sinus milieus what I talked about in my previous blog post. But other ones are Sigma-milieus, Limbic-types, Uranos Clåss.
You can also differ target groups in Market-related models. Think about Food, Living, Health, Cars, Finance, Fashion, Innovation.
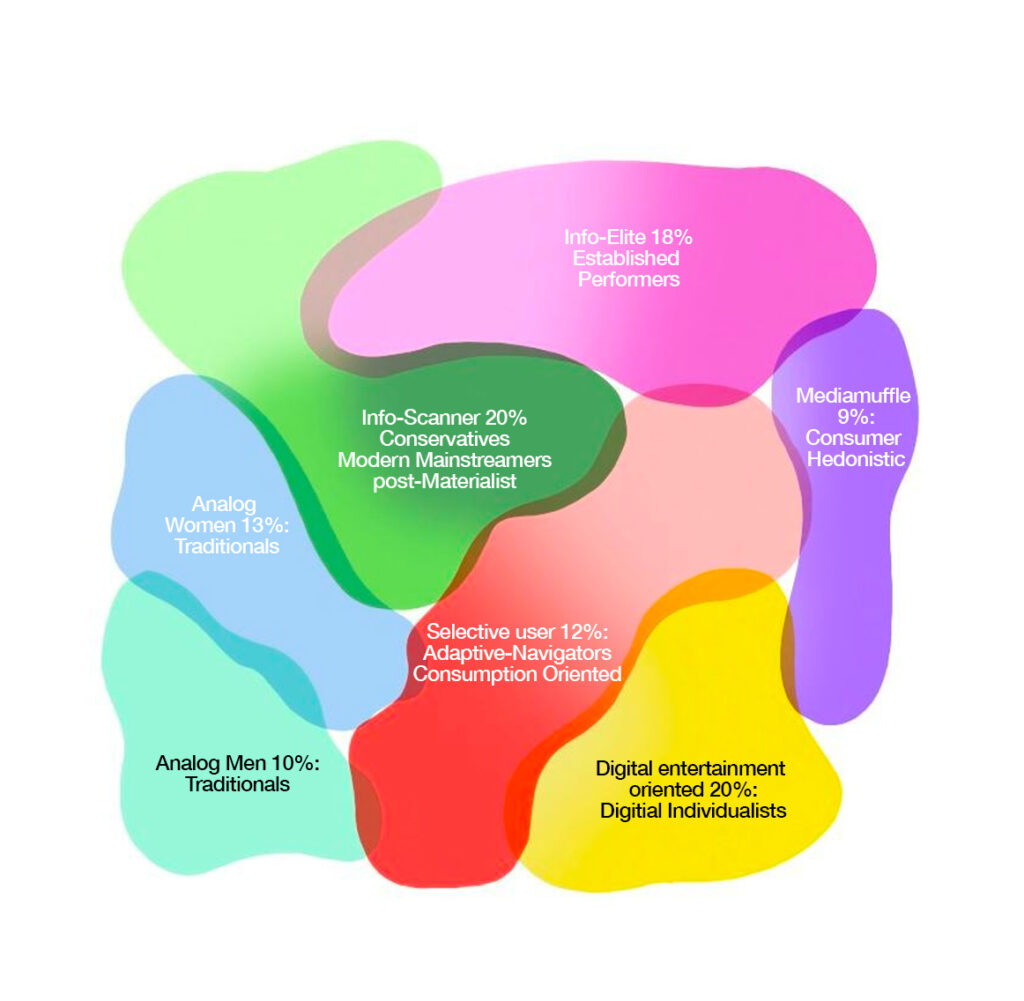
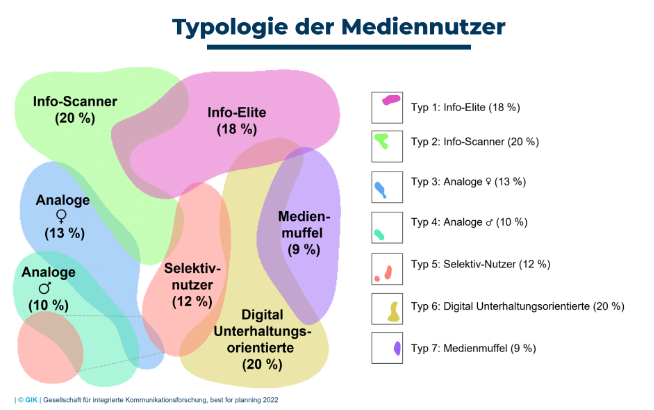
But Different target groups also means different type of media to approach them. (e.g. Magazines, newspapers, posters, TV, radio, internet, mobile and apps) these are each divided into 7 types that describe the intensity of the use of media. In this way, the media planner can see at a glance wheter his target group tends towards the preferred medium or not.
Type 1 Info Elite 18%:
Gets information several times a day and expect a wide range of news form various information sources. Newspaper and other printed media. Willing to pay for journalistic offers on the internet. Product suggestions from influencers. Podcast are used on a wide range of topics. They network professionally and privately via social media
Demographic info:
from 20 to middle age high level of education and high income, time independent. Woman and men are equally represented.
Type 2 Info scanner 20%:
Media consumed several times a day as a trusted source of information from this well-educated, highincome guy. Analoge and digital. Print plays a important role in their routine. Political, economic and cultural topics arouse the most interest. But health, nature and DIY are also important. Social networks and internet are used carefully with focus on data protection to maintain private contacts.|
Demographic info:
Older age group 50+ years old
Type 3 analog ♀ 13%:
daily use of newspaper and television. Most focus on handcrafts, cooking, celebrities. There is also a big interest in folk music, telenovelas and homeland movies. Media use is based on entertainment and escapism. Paper is still important, for example the weekly magazines. While the internet, tablets and smartphones are hardly used.
Demographic info:
age: begin 60s people over 70 are well represented. female dominated. Rather low-educated, low income
Type 4 analog ♂ 10%:
Regional daily newspaper and television. Likes to find out about regional topics, sports or politics and like to watch Krimis and folk music programs. Social media is almost non existing
Demographic info:
Age: begin 60s people over 70 are well represented. male dominated. Rather low-educated, low income. Often retired
Type 5 selective user 12%:
Topics such as sports, cars and computers are very popular with the predominantly male type. Diversity of information and trustworthy sources are less important. They often use streaming platforms, linear television, topic-related magazines. Fictitious series are also part of their everyday life.
Common social media are used to maintain contacts while business networks are irrelevant.
a part of the selective users uses both digital and analog distribution channels.
Demographic info:
Either very young or middle-aged
Type 6 digital entertainment oriented 20%:
Focus on shows, soaps entertainment and lifestyle access through video and audio streaming. Influencers and bloggers also provide strong impulses and to buy on social media. Messenger services and Instagram are used more frequently to make and maintain contacts than networks like LinkedIn. Fast availability as well as time and location-independent media use via smartphone and tablet are of great importance. In case of print, is this target group in minority unless some persons are interested in some segments of print.
Demographic info:
Young mostly student
Type 7 mediamuffle 9%:
They have no special expectations of the media and use all media under-proportionally.
Demographic info:
Middle-aged cohorts are disproportionately represented, men and women to the same extent. Low educational qualifications or some are still in training. Income is low.
Sources:
Zielgruppen •. (2022, October 4). Gesellschaft Für Integrierte Kommunikationsforschung. https://gik.media/best-4-planning/zielgruppen/
Marktstudien •. (2022, October 4). Gesellschaft Für Integrierte Kommunikationsforschung. https://gik.media/best-4-planning/marktstudie/
Mediaplanung •. (2022, November 28). Gesellschaft Für Integrierte Kommunikationsforschung. https://gik.media/best-4-planning/mediaplanung/