This article seek to present and overiew of the implementation of ehealth in Benin to help us see the opportunities and challenges we might face while trying to present a contextualized framework to “Designing an eHealth App for Sustainable Healthcare in Benin” that can contribute to improve community health but also support the National eHealth Strategy in Benin .

Zouléha Karimou, a 35-year-old housewife and mother of five boys, takes part in a bednet demonstration in her village of Sibongou in the health zone of Bariénou, about 500 kilometers north of Cotonou, Benin, on June 17, 2018
Source: JSI- Improving Community Health in Benin | by JSI | Medium
The implementation of eHealth in Benin Republic has been driven by the National eHealth Strategy, which aims to improve the country’s healthcare sector through the use of information and communication technology (ICT). The strategy was adopted in November 2017 and covers the period from 2018 to 2022. The key components of the strategy include the establishment of an eHealth infrastructure, strengthening human resources for health, improving access to healthcare services, enhancing healthcare quality and patient safety, and developing a legal and regulatory framework.
The situational context in Benin Republic reveals that eHealth initiatives have been implemented in the country in the past, mainly through private projects supported by NGOs, international organizations, or bilateral cooperation. However, the Ministry of Health had limited engagement in these programs, and many of them faded away due to a lack of funding and little assessment of their impact on the health system.
To institutionalize the use of digital health, the Ministry of Health assigned the Department of Information Technology and Pre-archiving to develop a national eHealth plan. Two strategic documents on the use of ICT in health have been created. However, the review in 2015 highlighted the lack of a nationwide and uniform network for the Ministry of Health, limited connectivity of health structures, and a lack of ICT infrastructure, particularly in rural areas.
Despite these challenges, the government of Benin has shown strong commitment to eHealth. The national eHealth strategy includes best practices such as government commitment, a favorable institutional and legislative framework, the development of a national eHealth master plan, and engagement with health professionals and the private sector. Lessons learned from previous projects and initiatives are also being applied to the strategy’s implementation.
The national eHealth strategy aims to establish an eHealth infrastructure, enhance human resources for health, improve access to healthcare services, enhance healthcare quality and patient safety, and develop a legal and regulatory framework. The strategy includes the creation of a national health information system, the use of telemedicine, and the development of eLearning programs for healthcare worker training.
The implementation of the strategy faces various challenges, including a lack of funding, insufficient technical human resources, delays in legal and regulatory aspects, poor user confidence, limited ICT infrastructure, and low accessibility to health structures. However, the government’s commitment, favorable institutional environment, and qualified human resource pool provide a solid foundation for the strategy’s implementation.
To ensure accountability and transparency, the strategy has established a monitoring and evaluation system to track the implementation of projects and their impact on the health system. Impact indicators are being developed, and an independent team is responsible for collecting and analyzing these indicators. The strategy also emphasizes the involvement of health professionals and the private sector in the implementation process.
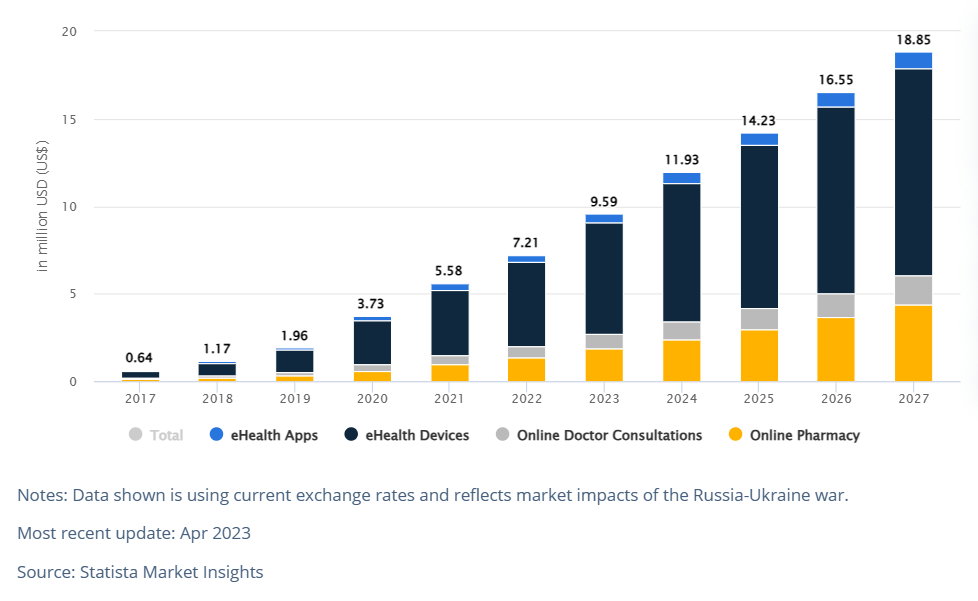
In Benin, the eHealth segment is expected to show positive growth and development. The revenue in the eHealth segment is projected to reach US$9.59 million by 2023. Furthermore, there is an estimated annual growth rate (CAGR 2023-2027) of 18.42%, which would result in a projected market volume of US$18.85 million by 2027. User penetration in the eHealth segment is expected to be 7.77% in 2023, and it is projected to increase to 12.33% by 2027. This indicates a growing adoption of eHealth solutions by the population in Benin. The average revenue per user (ARPU) is anticipated to be US$9.40, reflecting the potential value and monetization opportunities within the eHealth market in Benin. It is worth noting that in global comparison, China is expected to generate the highest revenue in the eHealth segment, with an estimated revenue of US$23,270 million in 2023. These figures highlight the potential and growth prospects of the eHealth segment in Benin, indicating increasing adoption and revenue generation in the coming years.
In conclusion, while challenges exist, Benin Republic is committed to using eHealth to improve its healthcare system. The strategy’s implementation is supported by a favorable institutional and legislative environment, government commitment, and lessons learned from previous projects. With continued efforts and addressing the challenges, eHealth has the potential to improve healthcare access and quality in Benin Republic. The eHealth segment in Benin is poised for significant growth and offers promising opportunities for improving healthcare accessibility and enhancing overall health outcomes in the country.
Reference:
- Y. A. A. Sossou, “Status of eHealth in Benin republic,” March 2023. https://www.intgovforum.org/en/filedepot_download/278/24571.
- https://jsihealth.medium.com/improving-community-health-in-benin-842df2bcadca
- https://www.statista.com/outlook/dmo/digital-health/ehealth/benin
- www.itu.int
- www.sante.gouv.bj
- www.who.int