The animation industry has evolved for over a century, with several animation studios emerging across the world. Generally, animation studios are companies that create animated media for different purposes. There are different types of animation studios – on the one hand there are large corporate animation studios that develop and distribute their own intellectual properties (for example animated films), thus owning the rights to the technologies and characters they created. Large animation corporations, such as The Disney Corporation, often own multiple subsidiary studios (Disney, for example owns Walt Disney Animation Studio, 20th Century Animation or Pixar Animation Studios), and are made up of a number of specialized departments and units. As these companies tend to work with high standards in terms of technologies and equipment, they are well-suited for working on high budget productions or films that require certain special techniques. Other companies, on the other hand, work for clients on a contract basis. Small contractor studios are often private-owned businesses and create animated content while not owning the digital merchandise copyrights. (cf. deedeecourse, n.d.)
Over the course of the past couple of decades and even in recent years, the animation industry has seen a rapid growth and development. In 2021 alone, the global animation market grew by five percent to more than 372 billion U.S. dollars, reflecting the constantly rising demand for animated content. For example, six out of 10 of the highest-grossing animated movies in North American history originated from the mid to late 2010s. (cf. Statista Research Department, 2023)
The studios with the top-grossing animated feature films of all time are Disney, Pixar (run by Disney since 2006) and DreamWorks. (cf. Statista Research Department, 2023)
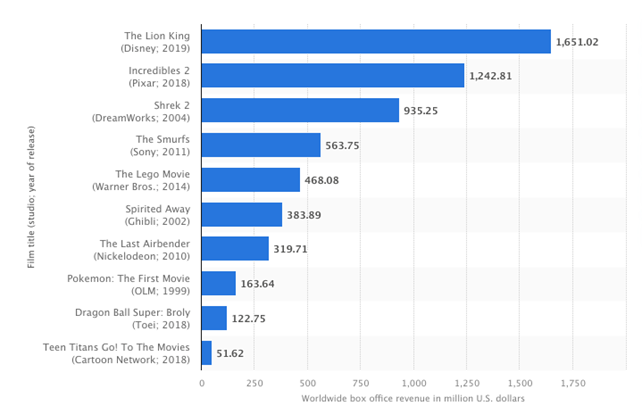
The following paragraphs will include a couple of facts about one of the world’s largest animation corporations and the animation studios owned by it: The Walt Disney Company.
Founded in 1923 as „Disney Brothers Cartoon Studios“, Disney is among the most successful animation companies today, owning subsidiary studios such as „Pixar“ and „Walt Disney Animation Studios“. Disney is very well known due to the fact that they set many of the standards and developed a number of animation techniques that are still being used today. (cf. Kizer, 2022)

Walt Disney Animation Studios is the Disney Company’s most successful animation studio, having produced movies like „Frozen“, „The Lion King“ or „Mulan“. Also, they were the ones to define the 12 principles of animation and developing the multiplane camera, which then became a standard in traditional animation. (cf. Bailey, 2019)

Pixar is especially known for its computer-generated 3D animations (CGI), using its own rendering software „RenderMan“. (cf. deedeecourse, n.d.)
It is a renderer developed by Pixar Animation Studios used for rendering VFX and animation. It has been the core rendering technology of the company for more than 30 years. (cf. Pixar, n.d.)
With „Toy Story“, Pixar released the world’s first feature-length computer animated feature film in 1995, receiving multiple Academy Awards for it, including Best Original Screenplay, making it the first animated film to be recognized for screenwriting. Other movie productions by Pixar include „Monster Inc.“, „Finding Nemo“, or „WALL-E“. The studio was bought by the Walt Disney Company in 2006. Other film studios owned by the Disney Company include 21st Century Fox, Lucasfilm Ltd., and Marvel Entertainment. (cf. Pixar, n.d.)

Sources
(1) deedeecourse (n.d.): Top 10 biggest animation studios in the world [online] https://www.deedeestudio.net/en/post/animation-studio [accessed on 26.01.2023]
(2) Statista Research Department (2023): Animation industry – statistics & facts [online] https://www.statista.com/topics/9725/animation-industry/#topicOverview [accessed on 26.01.2023]
(3) Statista Research Department (2023): Highest-grossing animated feature films of selected studios worldwide as of July 2022 [online] https://www.statista.com/statistics/1322150/highest-grossing-animated-movies-studio-worldwide/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]
(4) Kizer, Kristin (2022): The 10 Largest Animation Studios In The World [online] https://www.zippia.com/advice/largest-animation-studios/ [accessed on 26.01.2023]
(5) Bailey, Jason (2019): What Disney Risked to Make ‘The Lion King’ in 1994 [online] https://www.nytimes.com/2019/07/18/movies/disney-lion-king.html [accessed on 27.01.2023]
(6) Pixar (n.d.): What is RenderMan? [online] https://renderman.pixar.com/about [accessed on 26.01.2023]
(7) Pixar (n.d.): Our Story [online] https://www.pixar.com/our-story-pixar [accessed on 26.01.2023]
Image Sources
Figure 1: Statista Research Department (2023): Highest-grossing animated feature films of selected studios worldwide as of July 2022 [online] https://www.statista.com/statistics/1322150/highest-grossing-animated-movies-studio-worldwide/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]
Figure 2: Wright, Zander (2021): Longtime Disney Veterans Promoted at Walt Disney Animation Studios [online] https://insidethemagic.net/2021/10/walt-disney-animation-studios-promotions-zw1/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]
Figure 3: IMDb (n.d.): Frozen [online] https://www.imdb.com/title/tt2294629/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]
Figure 4: IMDb (n.d.): The Lion King [online] https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0110357/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]
Figure 5: IMDb (n.d.): Mulan [online] https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0120762/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]
Figure 6: IMDb (n.d.): Toy Story [online] https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0114709/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]
Figure 7: IMDb (n.d.): Finding Nemo [online] https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0266543/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]
Figure 8: IMDb (n.d.): WALL-E [online] https://www.imdb.com/title/tt0910970/ [accessed on 27.01.2023]