With the increasing concern about environmental sustainability and public health, there is a need to develop innovative solutions that promote sustainable healthcare practices. The healthcare industry has been under pressure to address the rising healthcare costs and environmental concerns, and the use of digital technology in healthcare has emerged as a potential solution. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in designing eHealth apps that not only improve the quality of healthcare but also contribute to a more sustainable future while encouraging users to adopt healthy behaviors while also reducing their environmental impact.
Interaction design principles can be used to motivate and engage users to adopt sustainable healthcare practices. For example, gamification, personalization, and social interaction elements can be integrated into the design of eHealth apps to promote healthy behaviors and encourage users to make sustainable choices. A study by Sutcliffe et al. [1] found that gamification elements such as points, leaderboards, and rewards can lead to increased user engagement and motivation in health-related apps. In their study, the authors investigate the role of gamification in promoting user engagement and motivation to adopt health apps. The study highlights the potential benefits of incorporating gamification elements into healthcare apps, such as increasing user satisfaction, promoting healthy behaviors, and enhancing the effectiveness of healthcare interventions. Their findings suggest that gamification can be a key determinant of the adoption of health apps, and thus, it is important to consider gamification as a design strategy in the development of eHealth apps for sustainable healthcare.
On the other hand, Tran et al.[2] provides a scoping review of the current state of evidence on the use of gamification and incentives in mobile health apps to improve medication adherence. While their foundings stressed out the lack of significance amount of evidence supporting the use of gamification and financial incentives to improve medication adherence, their paper highlights the potential benefits and drawbacks of these strategies and provides recommendations for future research.
A study conducted by Carlqvist et al. [3] provides valuable insights into the potential for eHealth applications to function as value-creating resources in healthcare from the perspective of healthcare professionals. The study was a qualitative interview study that explored healthcare professionals’ experiences with using an eHealth application and how it could create value in healthcare. The findings of the study are relevant to the topic of creating a sustainable future in healthcare through the process of designing an eHealth app. By understanding how an eHealth application can create value for healthcare professionals, designers can ensure that the app they design meets the needs and expectations of its users. Additionally, designing an app that creates value for healthcare professionals can lead to increased adoption and sustained use of the app, which can contribute to a more sustainable healthcare system in the long run.
Privacy and data security are important ethical considerations that need to be addressed in the design of eHealth apps as well. Health-related information is sensitive, and users need to trust that their data is secure and protected. Incorporating privacy and security measures in the design of eHealth apps is crucial to ensure user trust and adoption.
In this post we want to explore the process of designing sustainable eHealth apps, with a focus on the role of Interaction design and digitalization in promoting sustainability. To shed light on this topic, we have examined the works of Jansen [4], who discusses the importance of digitalization in healthcare and its potential impact on sustainability, Oderanti et al.[5], who examine business models for sustainable commercialization of eHealth innovations, and van Limburg and van Gemert-Pijnen [6], who propose innovative business models for sustainable eHealth applications.
After Analysis of those articles a question still subsisted: what is process of designing an eHealth app for a sustainable future in healthcare? In that regards we would like to propose the following these 8 steps:
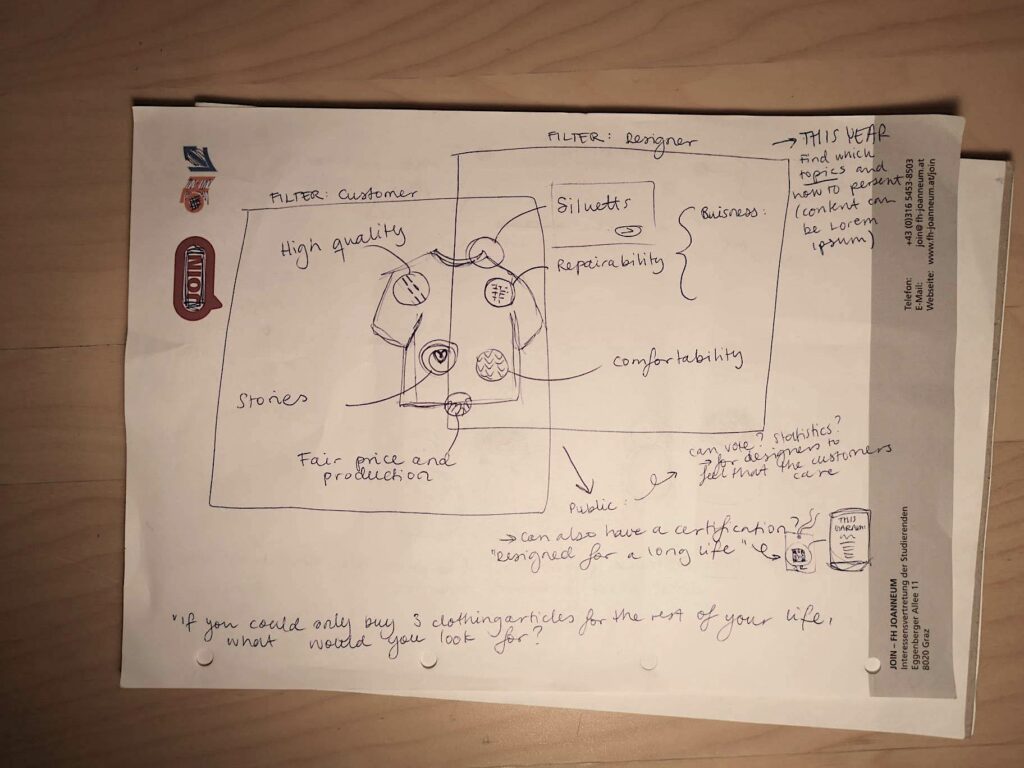
- Identify sustainability goals & the needs: In this first step you could conduct research and gather insights from potential users, healthcare providers, and other stakeholders on sustainability challenges in healthcare. For example , high rates of chronic diseases, lack of access to qualify care, environmental threats, etc [3].
- Define the scope with sustainability in mind: Once the sustainability goals have been identified, the next step is to define the scope of the app with sustainability in mind. This involves identifying sustainable features, functionality, and target audience. Defining the goals and objectives of the eHealth app, such as improving health outcoms, enhancing patient engagement, reducing costs, minimizing environmental impact, etc[4]
- Develop a business model that ensures the sustainability and scalability of the eHealth app, such as revenue streams, value proposition, customer segments, etc.[5]
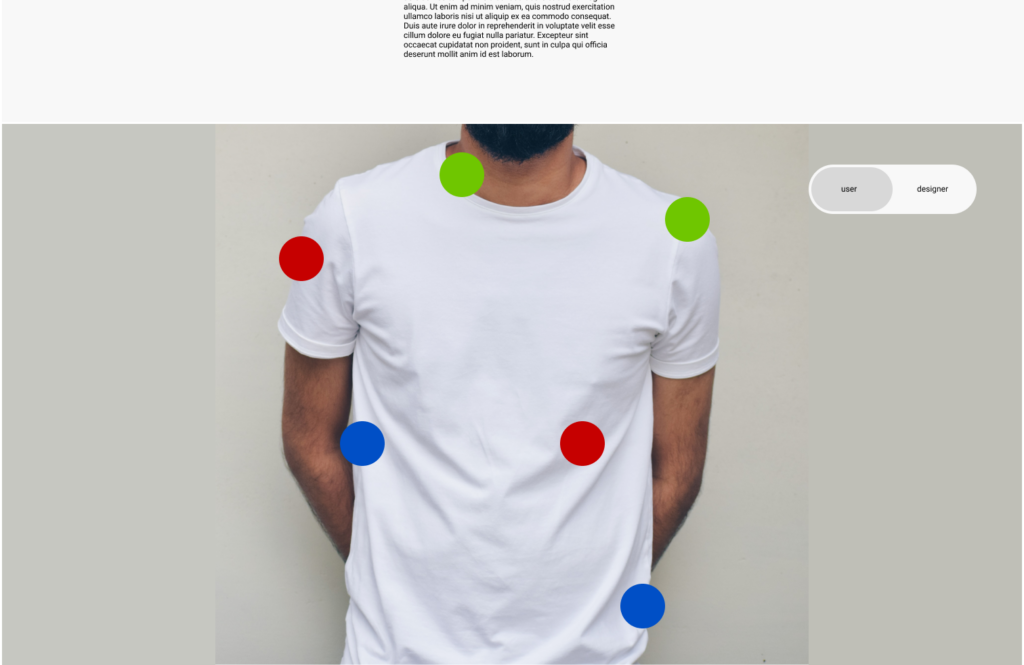
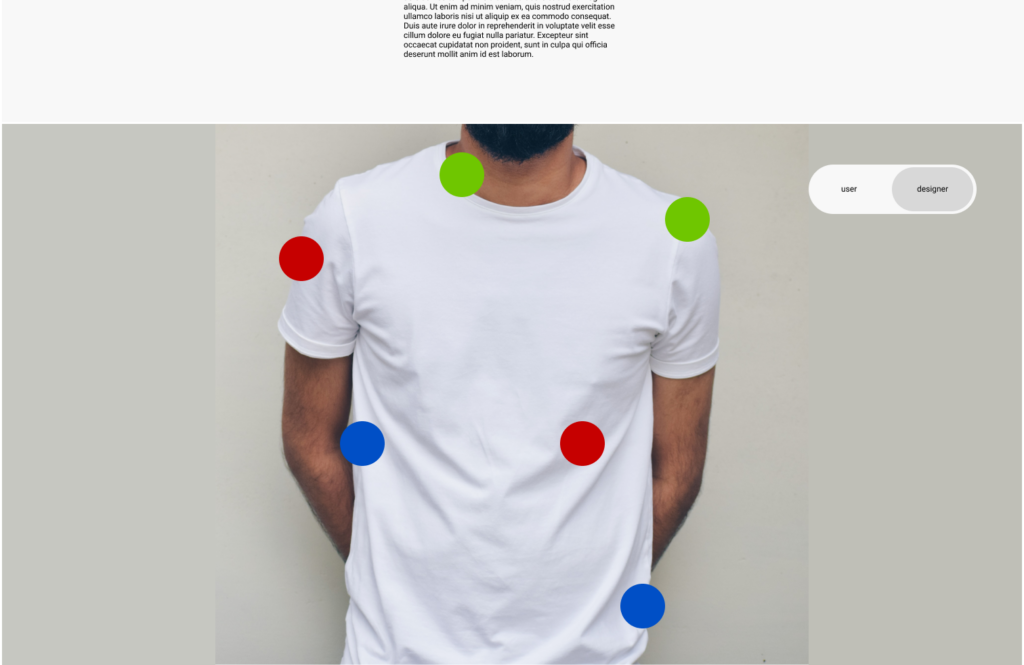
- Develop wireframes and prototypes with sustainability in mind: Wireframes and prototypes to visualize the app’s user interface and to test its sustainability impact. At this stage you come up with creating low-fidelity sketches or high-fidelity interactive prototypes with sustainability considerations in mind.
- Conduct user testing with sustainability in mind: This will help gather feedback on the app’s sustainability impact, as well as its usability and functionality. of course you can recruite participants to test the app and providing feedback on their sustainability experience.
- Develop the app with sustainable materials and practices: Once the wireframes and prototypes have been tested and refined, the app can be developed with sustainable materials and practices. This can involve using renewable energy sources, using recycled or biodegradable materials, or minimizing the app’s carbon footprint in other ways.
- Ensure regulatory compliance with sustainable regulations: eHealth apps designed for sustainable healthcare may be subject to regulations related to sustainability practices, data privacy, security, and healthcare compliance. Ensuring compliance may involve obtaining appropriate certifications or following specific standards related to sustainability.
- Launch and monitor sustainability impact: Once the app has been developed and tested, it can be launched. It’s important to monitor the app’s sustainability impact, as well as its performance and user feedback, to ensure it continues to meet sustainability goals and regulatory requirements. Implement and monitoring the eHealth app in the real-world setting and collecting feedback for improvement [5,6]
In conclusion, designing an eHealth app for sustainable healthcare is a promising solution to promote sustainable healthcare practices while also improving public health. Interaction design principles can be used to create engaging and motivating apps that encourage users to adopt healthy behaviors and make sustainable choices. Privacy and data security considerations are essential ethical considerations that need to be addressed in the design of eHealth apps.
References:
[1] Sutcliffe, A., Kaur, K., & Noronha, J. (2013). Gamification: A key determinant of adoption of health apps. Proceedings of the 2nd ACM SIGHIT International Health Informatics Symposium (pp. 571-580).
[2] S. Tran, L. Smith, S. El-Den and S. Carter, “The Use of Gamification and Incentives in Mobile Health Apps to Improve Medication Adherence: Scoping Review,” JMIR Serious Games, vol. 9, no. 1, p. e30671, 2021
[3] Carlqvist, C., Hagerman, H., Fellesson, M. et al. Health care professionals’ experiences of how an eHealth application can function as a value-creating resource – a qualitative interview study. BMC Health Serv Res 21, 1203 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-021-07232-3
[4] A. Jansen, “Healthcare and the environment: Why does digitalization matter?,” Innovation Matters, Philips, Aug. 26, 2021. [Online]. Available: https://www.philips.com/a-w/about/news/archive/blogs/innovation-matters/2021/20210826-healthcare-and-the-environment-why-does-digitalization-matter.html.
[5] Festus Oluseyi Oderanti, Feng Li, Marija Cubric, Xiaohui Shi,Business models for sustainable commercialisation of digital healthcare (eHealth) innovations for an increasingly ageing population,Technological Forecasting and Social Change,Volume 171,2021,120969, ISSN 0040-1625,https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120969. (https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0040162521004017)
[6] A. H. M. van Limburg and J. van Gemert-Pijnen, “Towards Innovative Business Modeling for Sustainable eHealth Applications,” 2010 Second International Conference on eHealth, Telemedicine, and Social Medicine, Saint Maarten, Netherlands Antilles, 2010, pp. 11-16, doi: 10.1109/eTELEMED.2010.30.